The solution – a native Australian disruption
- Hi1a is a peptide from venom of the Fraser Island funnel-web spider
- Hi1a is an exceptionally potent inhibitor of ASIC1a (IC50 500 pM). It is 20,000x more potent than best small-molecule inhibitor of ASIC1a and 15x more potent than opioids on their receptor.
- Hi1a is exceptionally stable in human serum and CSF
- Hi1a has no effects on other cardiac channels, including hERG
- Hi1a is effective in preventing ischemic* injury of heart and brain
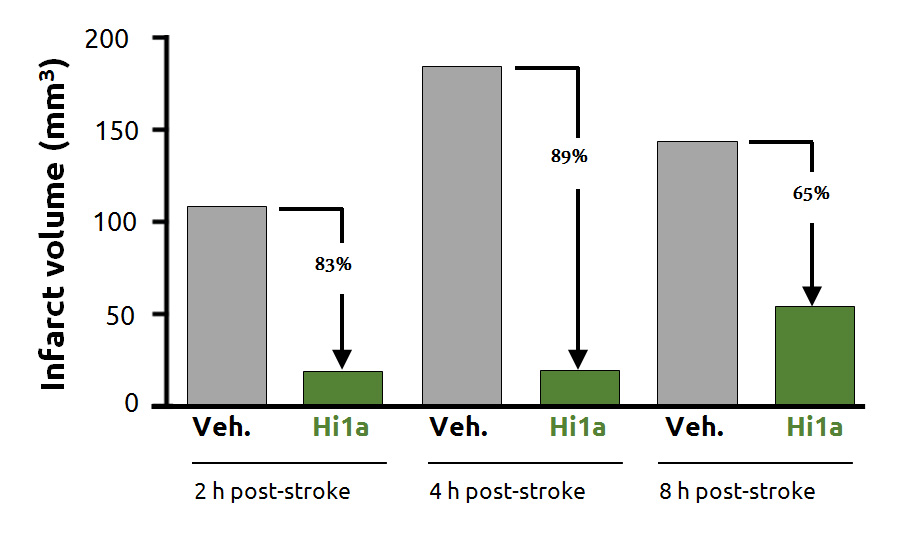
Hi1a protects brain even when given 8 hours after stroke onset
Single dose of Hi1a (2 ng/kg) administered i.c.v. 2 ,4, or 8 hours after stroke
Chassagnon et al. (2017) PNAS 114: 3750–3755

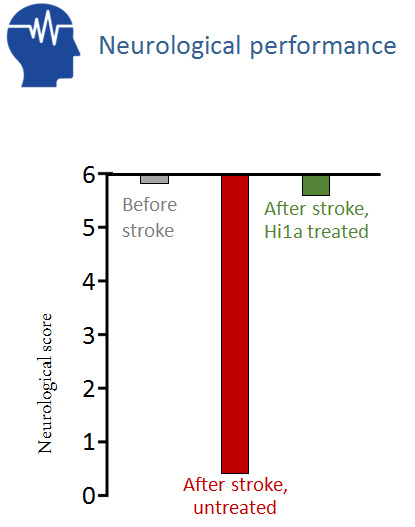
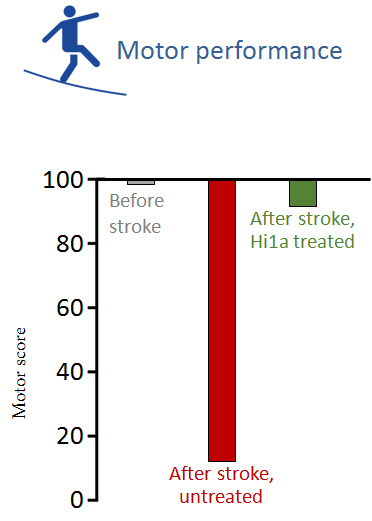
Hi1a greatly enhances functional recovery after stroke
Hi1a will be a game-changer for stroke
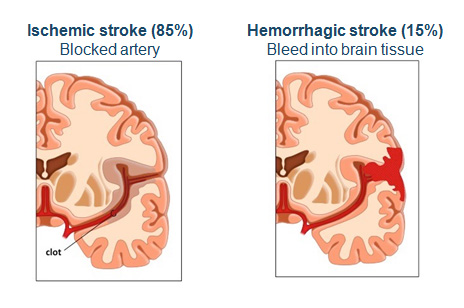
- The only drug currently available for stroke is the clot-busting drug tPA. Because of its mechanism of action, it is contraindicated for hemorrhagic stroke.
- Stroke patients cannot receive tPA until their brain is imaged in a hospital. This is a huge problem as 2 million brain cells die every minute after stroke onset.
- Because of its small therapeutic window (4 hours post-stroke) and its potential to induce an intracranial hemorrhage, only 5% of ischemic stroke patients receive tPA.
- Hi1a is not a clot-busting molecule. It is safe for all types of stroke, and thus it is suitable for administration by first responders.
- Administration by first responders will save lives and improve outcomes for survivors.
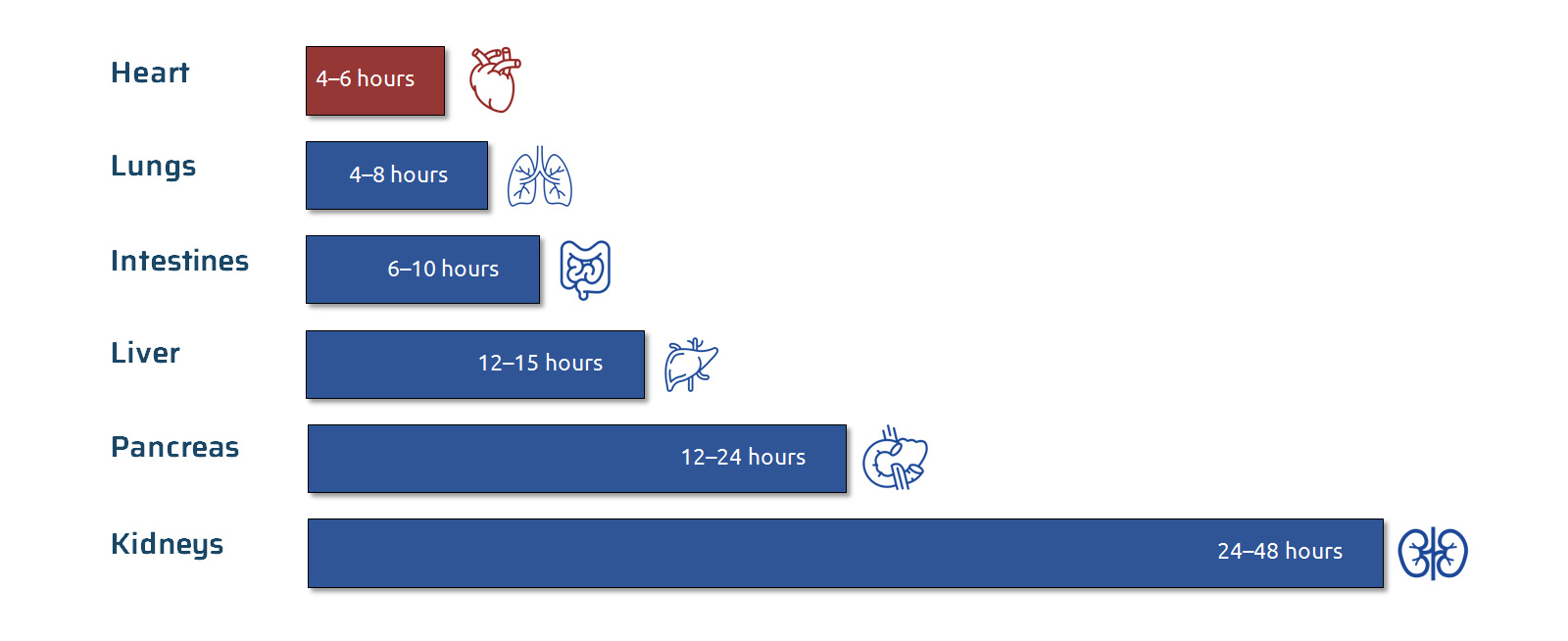
Organ susceptibility to ischemic injury: preservation times
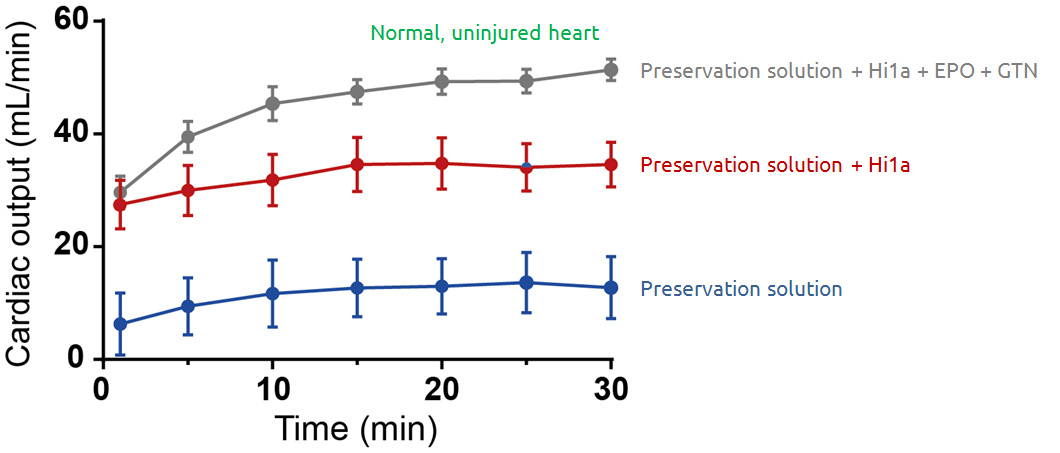
Hi1a protects donor hearts destined for transplantation
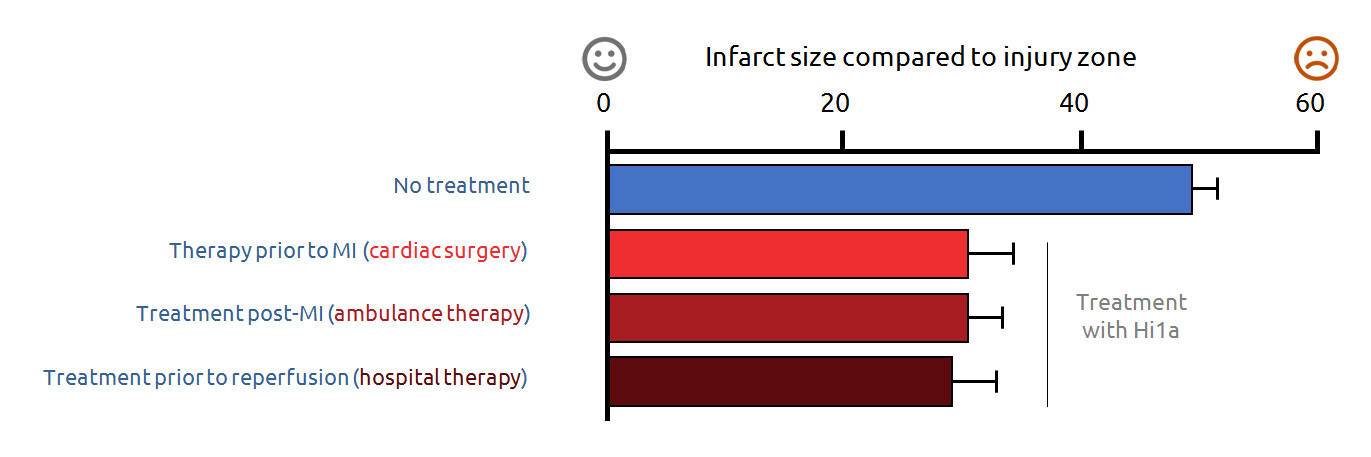
Hi1a protects heart muscle cells during a heart attack
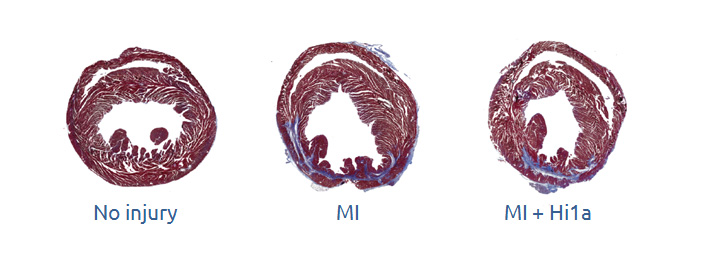
Cross-sections of mouse hearts with blue showing regions of fibrosis